Time#
The time module is used to convert Timestamp enumerated values into formatted strings, and vice versa. For example, the following will print each entry’s built-in timestamp value using the specified format and save the result as a string in a new enumerated value named “formattedTS”:
time -oformat "Mon Jan _2 15:04:05 2006 MST" TIMESTAMP formattedTS
If the first enumerated value argument is a string rather than a timestamp, the module will instead attempt to parse the string as a time and save the output into a Timestamp enumerated value. Note that if no specific format is given, the module will use the timegrinder library to try many possibilities. The following will look at a string enumerated value named “tsString” and attempt to convert it to a timestamp, placing the result in “extractedTS” if successful.
time tsString extractedTS
Supported Options#
-iformat <format>: Specifies the format to be used parsing strings. The format consists of a string representation of a specific time, “Mon Jan 2 15:04:05 MST 2006”, as used by the Go time library. Refer to the linked documentation for more examples. Note: This flag is ignored if the EV type is a timestamp.-oformat <format>: Specifies the format to be used when printing timestamps. The format consists of a string representation of a specific time, “Mon Jan 2 15:04:05 MST 2006”, as used by the Go time library. For instance, one may say-oformat "Mon 3:04PM"to get a very brief timestamp format. Refer to the linked documentation for more examples. Note: When using this flag, the output EV will be a string. When omitted, the output EV will be a timestamp type.-tz <timezone>: Specifies a time zone, in tz database format, e.g. “America/Denver”, “UTC”, or “Atlantic/Reykjavik”. This time zone will be used when printing timestamps (which do not have a time zone associated with them) and when parsing strings which do not contain a time zone specification.
Examples#
To print entry timestamps in a specific format and time zone:
tag=json time -oformat "Mon Jan _2 15:04:05 2006 MST" -tz "America/Chicago" TIMESTAMP foo | table TIMESTAMP foo
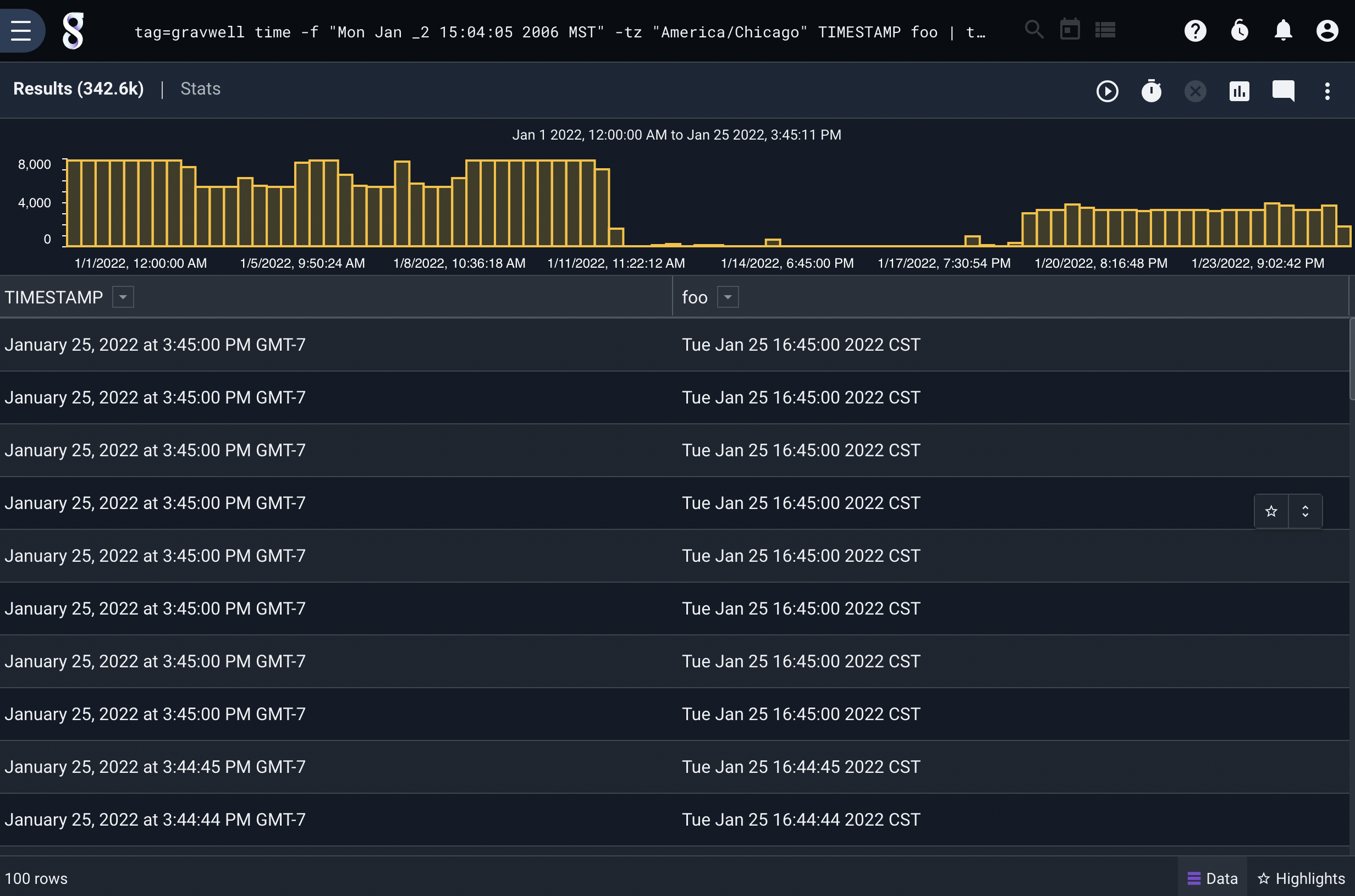
The output of the previous module invocation can be fed back in to the time module to convert back into timestamps:
tag=json time -oformat "Mon Jan _2 15:04:05 2006 MST" -tz "America/Chicago" TIMESTAMP foo | time -iformat "Mon Jan _2 15:04:05 2006 MST" -tz "America/Chicago" foo bar | table TIMESTAMP foo bar
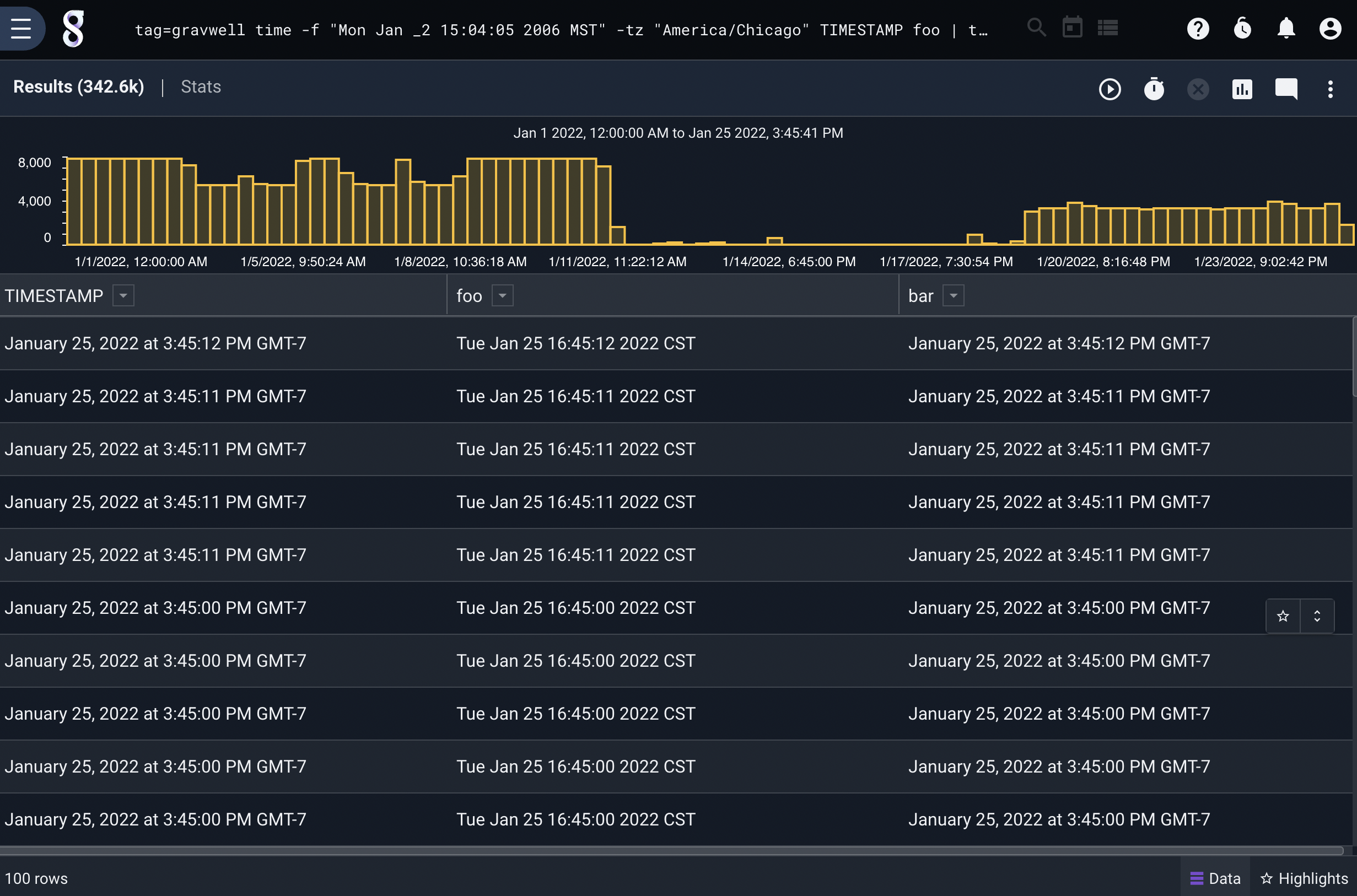
Note that the fractional seconds are truncated in the final output, because the intermediate time format does not include them.