Split#
The split module lets you split the contents of an entry or enumerated value into multiple entries.
Supported Options#
Specifying a name following any options informs the split module that it should split the named enumerated value rather than the contents of the entry itself. Omitting a name will cause it to operate on the entry.
-d <delim>: specify the delimiter. This can be a single character such as a semicolon, or a string–even a string with spaces, provided you wrap it in quotes.-clean: tells the module that after splitting the data, it should clean up tabs, spaces, and quote characters from the left and right ends of each string. Thus the entry containingfoo ,'bar', bazwould be split into three entries containingfoo,bar, andbaz.
Example Usage#
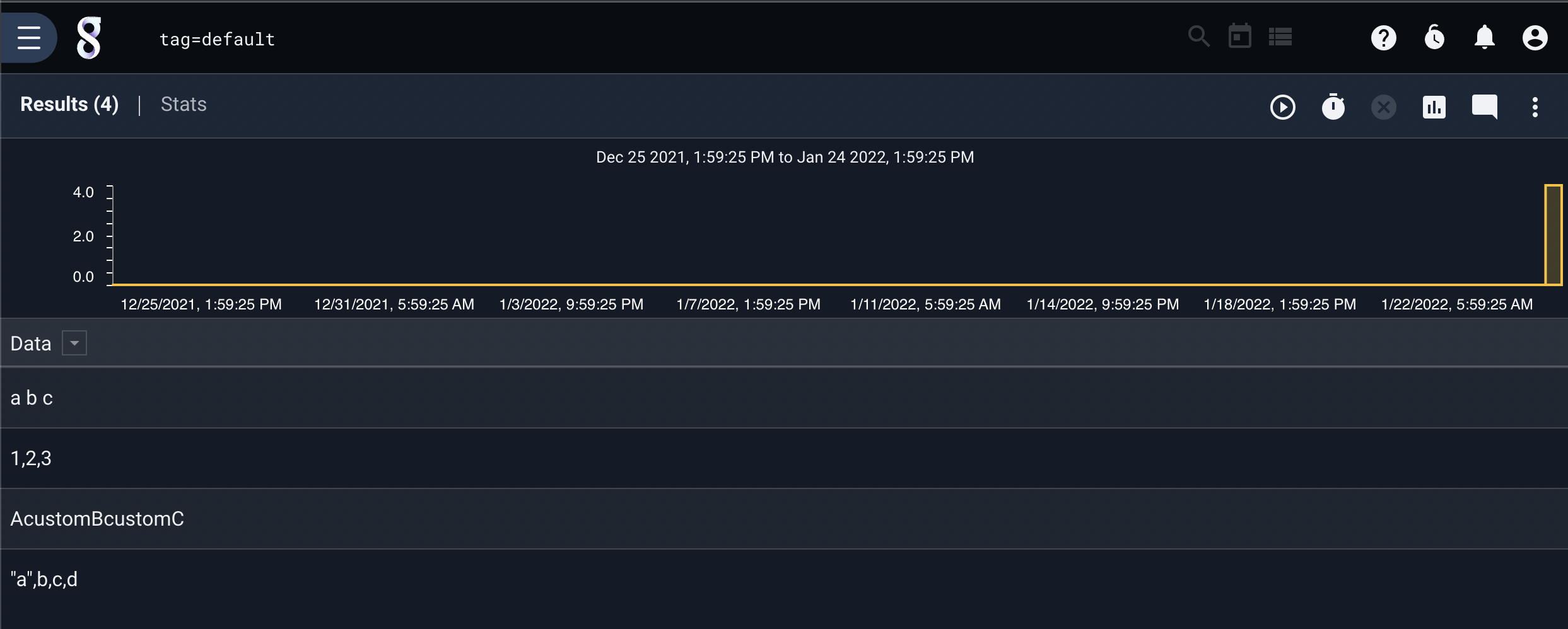
For these examples, we will consider the following example entries:
Basic splitting#
Specifying the split module with no additional arguments will split the entries based on the default delimiter, the comma:
tag=default split
Using the clean flag#
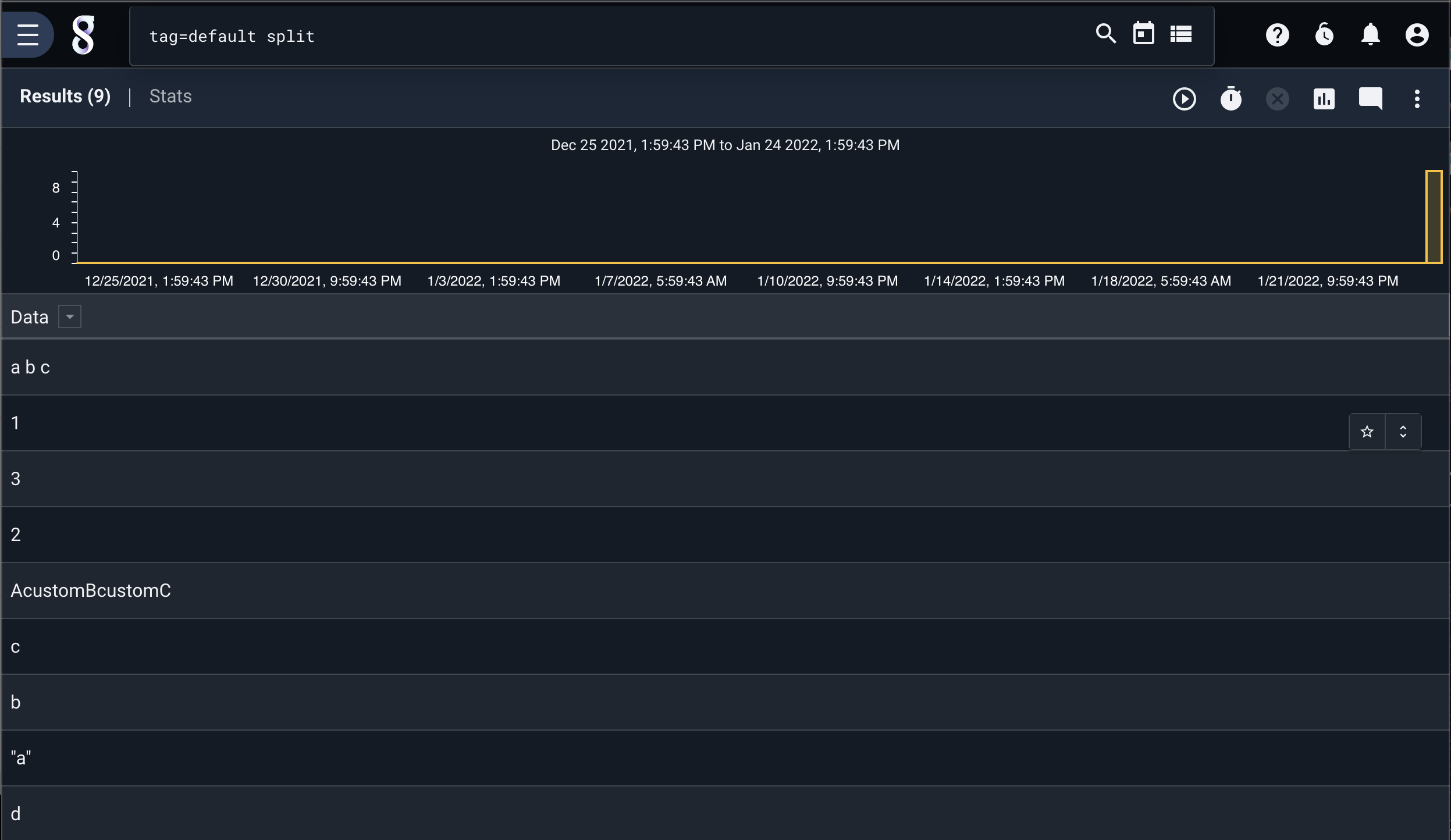
If we add the -clean flag, we note that trailing/leading quote marks and whitespace are eliminated:
tag=default split -clean
Specifying a delimiter#
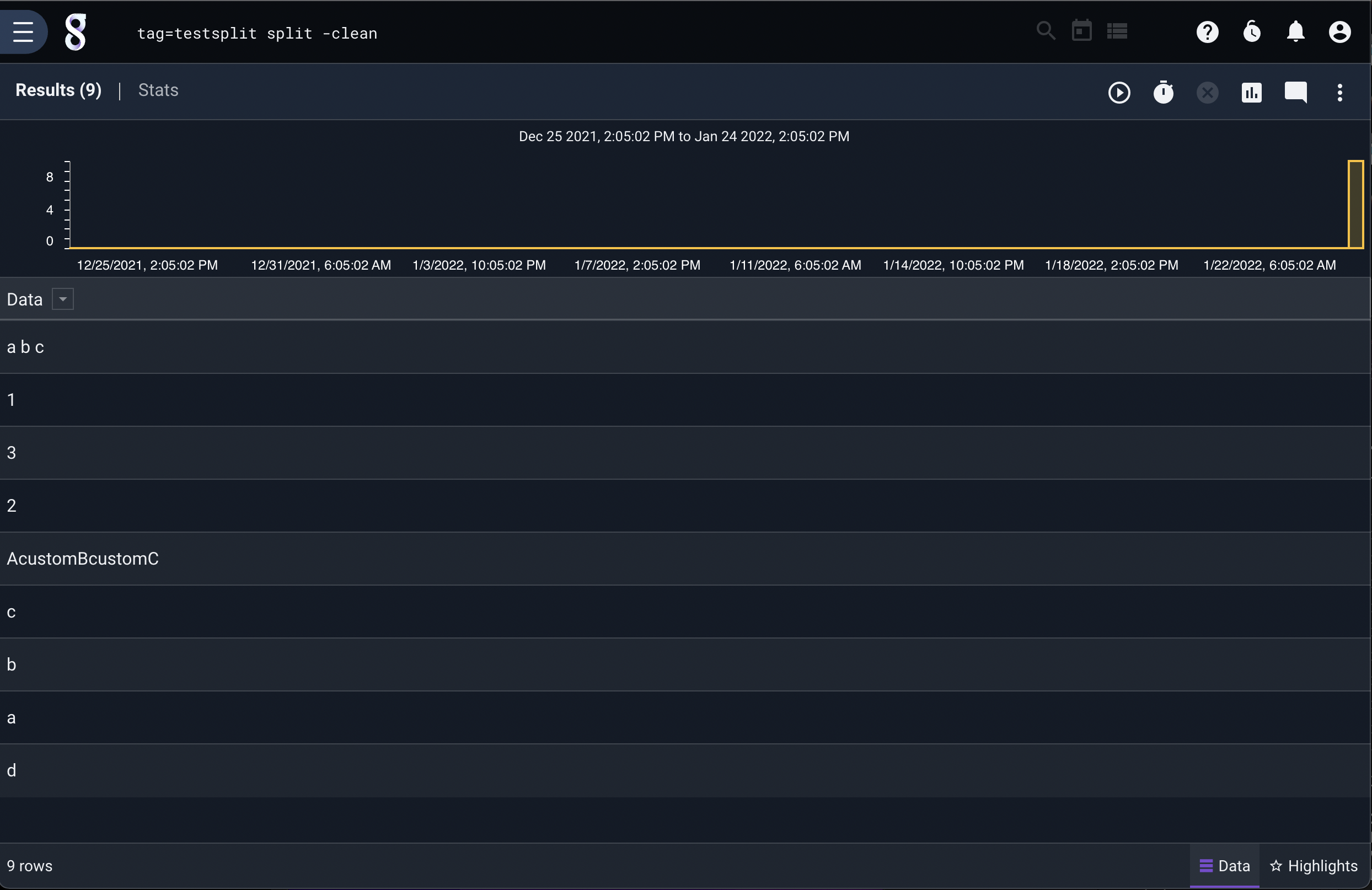
Some of the entries contain spaces. We can split on that using the -d flag:
tag=default split -d " "
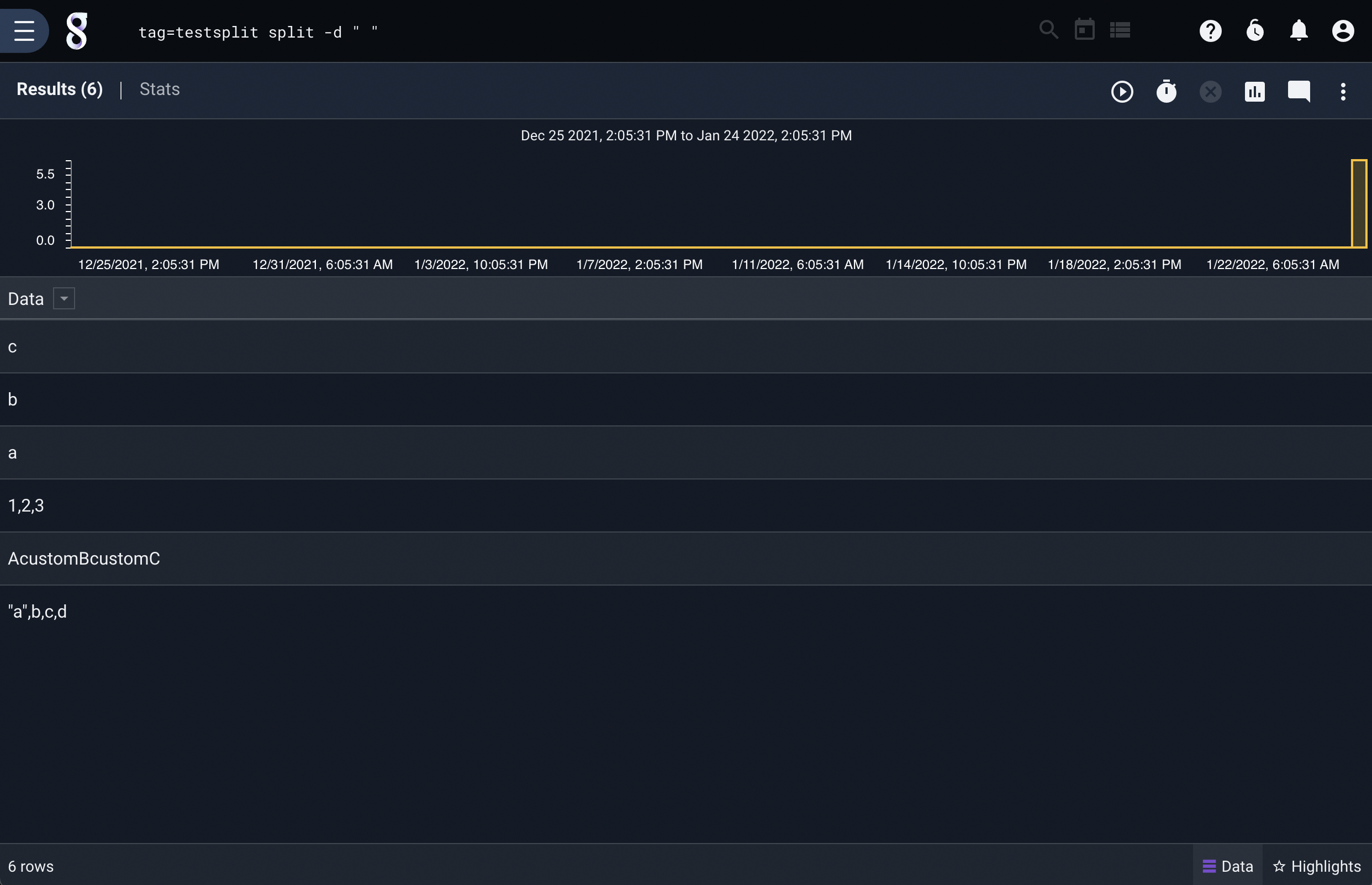
Note that one entry, a b c was cleanly split into 3 entries because it had a tab between every field, while another entry, "a", b, c ,d' was split into two because it contained a single tab character between ‘c’ and ‘,’.
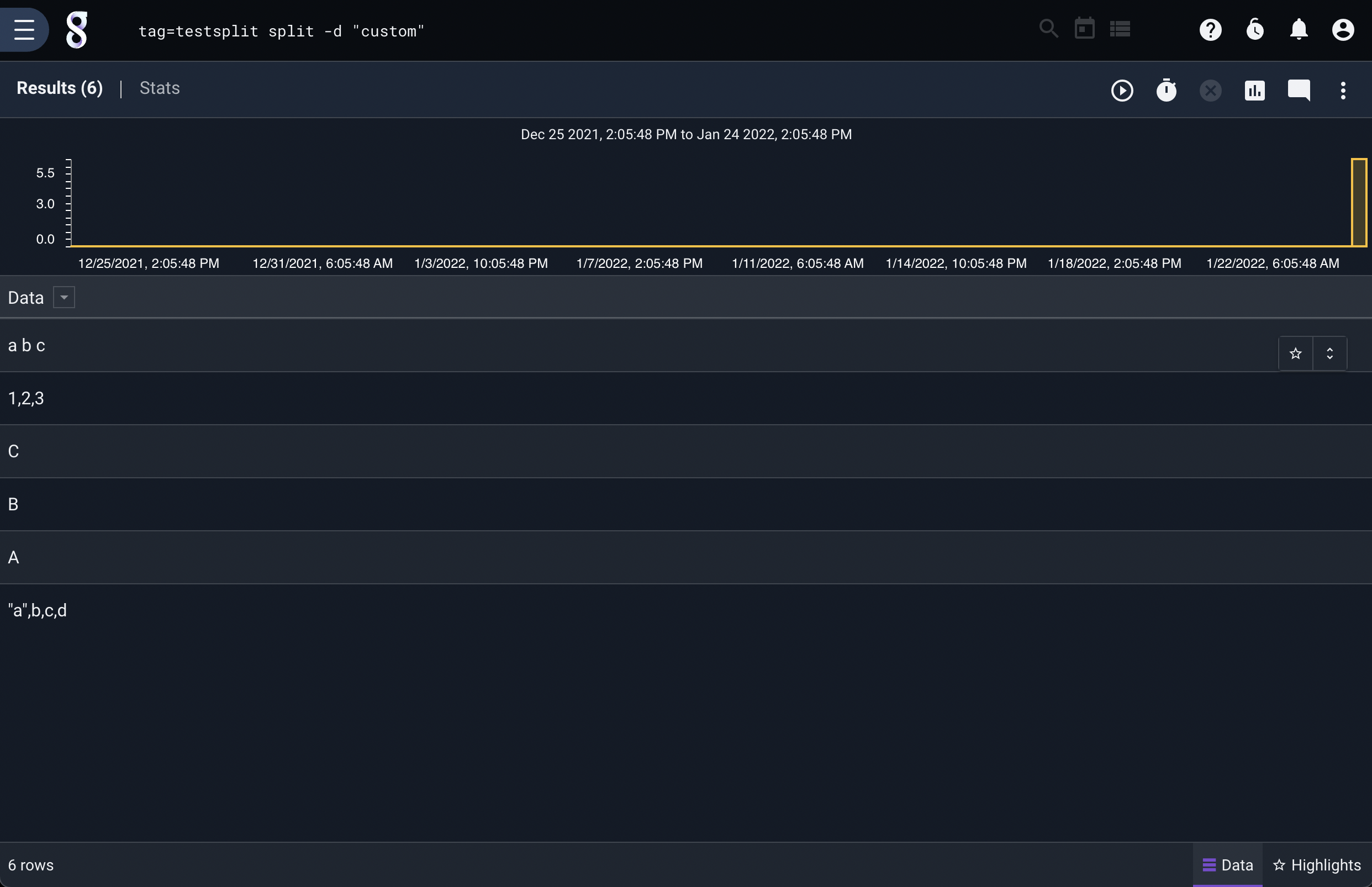
We can also specify arbitrary strings to use as delimiters:
tag=default split -d custom
Example Usage with Enumerated Values#
For this example, we will use Apache webserver log entries.
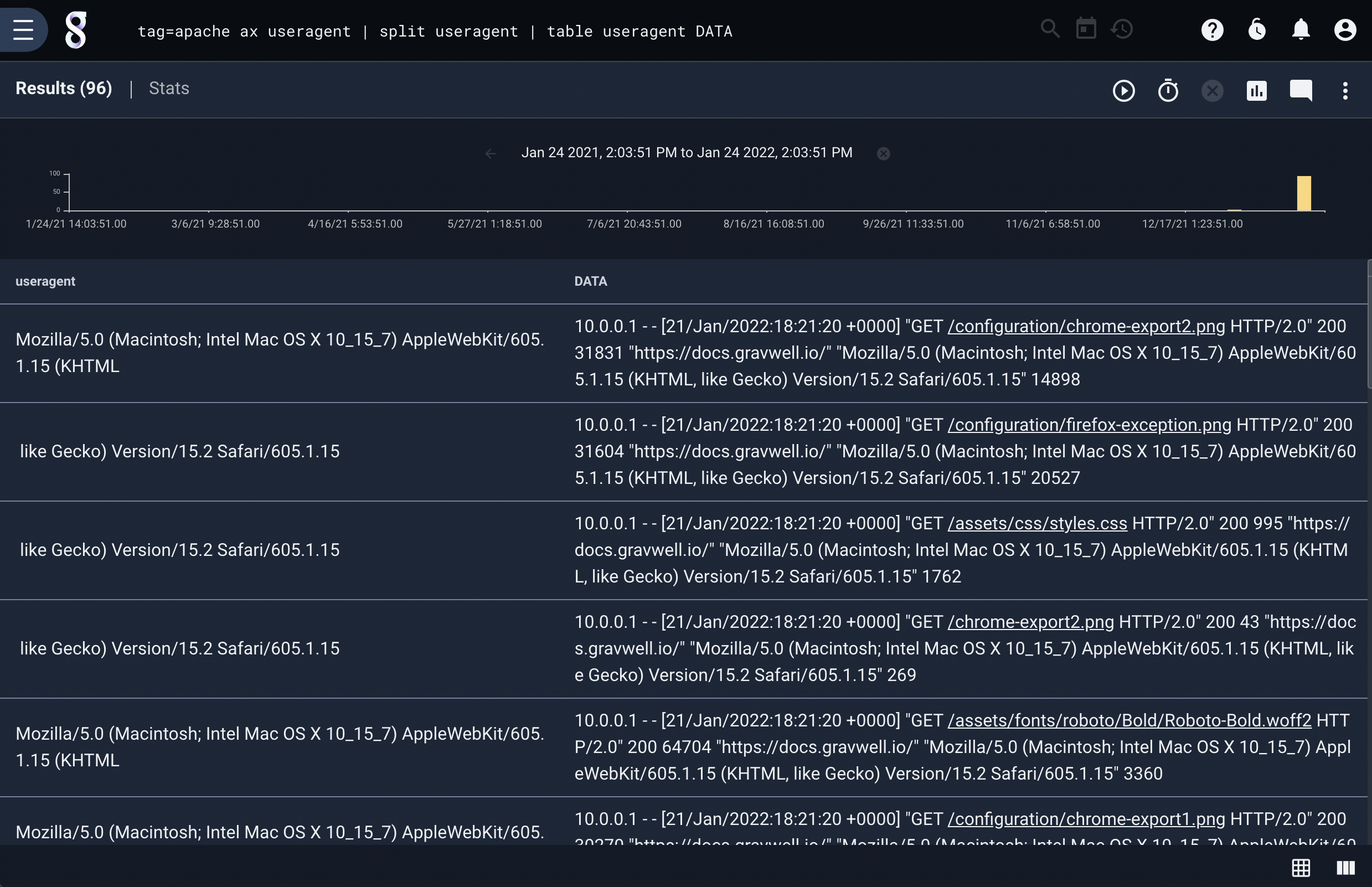
We can extract the ‘useragent’ field from the apache structure, then split it on commas:
tag=apache ax useragent | split useragent | table useragent
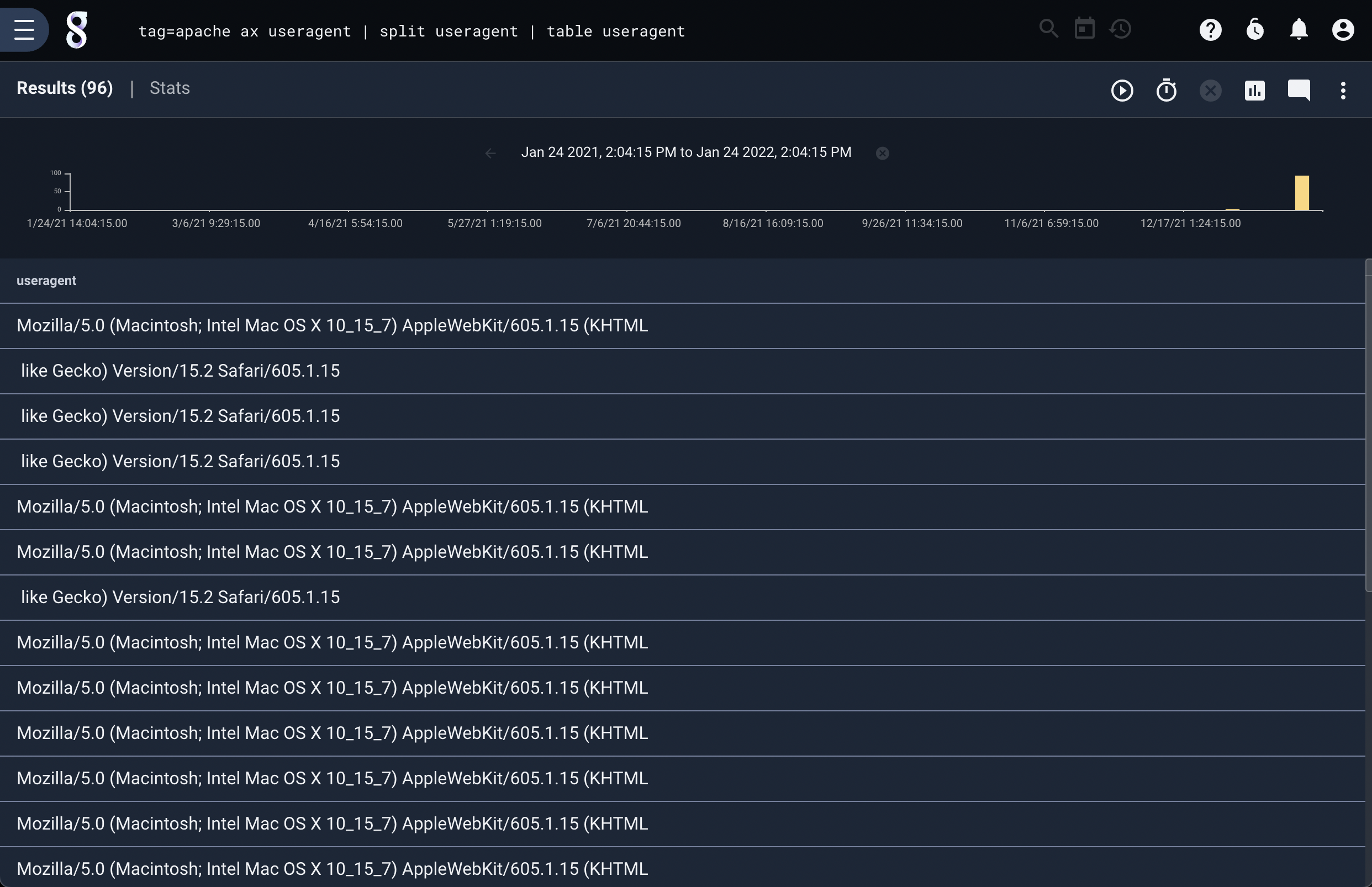
Note that the raw contents of the entries are not modified:
tag=apache ax useragent | split useragent | table useragent DATA