Ingest Preprocessors#
Sometimes, ingested data needs some additional massaging before we send it to the indexer. Maybe you’re getting JSON data sent over syslog and would like to strip out the syslog headers. Maybe you’re getting gzip-compressed data from an Apache Kafka stream. Maybe you’d like to be able to route entries to different tags based on the contents of the entries. Ingest preprocessors make this possible by inserting one or more processing steps before the entry is sent up to the indexer.
Preprocessor Data Flow#
An ingester reads raw data from some source (a file, a network connection, an Amazon Kinesis stream, etc.) and splits that incoming data stream out into individual entries. Before those entries are sent to a Gravwell indexer, they may optionally be passed through an arbitrary number of preprocessors as shown in the diagram below.
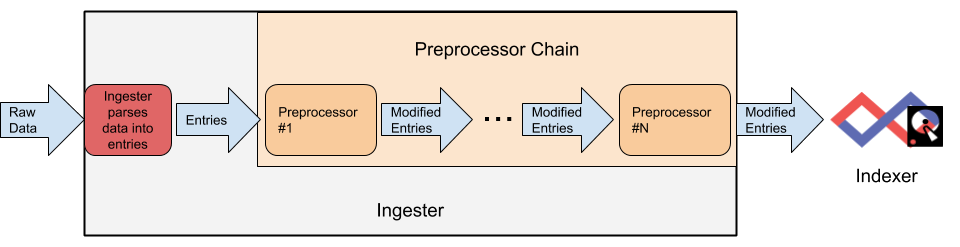
Each preprocessor will have the opportunity to modify the entries. The preprocessors will always be applied in the same order, meaning you could uncompress the entry’s data, then modify the entry tag based on the uncompressed data.
Configuring Preprocessors#
Preprocessors are supported on all packaged ingesters. One-off and unsupported ingesters may not support preprocessors.
Preprocessors are configured in the ingester’s config file using the preprocessor configuration stanza. Each Preprocessor stanza must declare the preprocessor module in use via the Type configuration parameter, followed by the preprocessor’s specific configuration parameters. Consider the following example for the Simple Relay ingester:
[Global]
Ingester-UUID="e985bc57-8da7-4bd9-aaeb-cc8c7d489b42"
Ingest-Secret = IngestSecrets
Connection-Timeout = 0
Insecure-Skip-TLS-Verify=true
Cleartext-Backend-target=127.0.0.1:4023 #example of adding a cleartext connection
Log-Level=INFO
[Listener "default"]
Bind-String="0.0.0.0:7777" #we are binding to all interfaces, with TCP implied
Tag-Name=default
Preprocessor=timestamp
[Listener "syslog"]
Bind-String="0.0.0.0:601" # TCP syslog
Tag-Name=syslog
[preprocessor "timestamp"]
Type = regextimestamp
Regex ="(?P<badtimestamp>.+) MSG (?P<goodtimestamp>.+) END"
TS-Match-Name=goodtimestamp
Timezone-Override=US/Pacific
This configuration defines two data consumers (Simple Relay calls them “Listeners”) named “default” and “syslog”. It also defines a preprocessor named “timestamp”. Note how the “default” listener includes the option Preprocessor=timestamp. This specifies that entries coming from that listener on port 7777 should be sent to the “timestamp” preprocessor. Because the “syslog” listener does not set any Preprocessor option, entries coming in on port 601 will not go through any preprocessors.
Testing Preprocessors#
The preprocessortest program is an open source tool to provide a simple scaffolding for testing ingest preprocessor stacks. It is designed to accept a data export from Gravwell and run the raw data through a set of preprocessors without actually ingesting any data.
Getting Started#
First, you will need to get a raw data export from some unprocessed data; this can be a simple text file that is line delimited or a JSON export of data from Gravwell. For example, if we were working with syslog data from the syslog tag we might run the following query:
tag=syslog limit 1000 | raw
Example Test Config#
An example stack of preprocessors may have a configuration file like so:
[Global]
Preprocessor=apprtr
Preprocessor=loginapp
[Preprocessor "apprtr"]
Type=syslogrouter
Template=`syslog-${Appname}`
[Preprocessor "sshattach"]
Type=regexextract
Regex=`Failed password for( invalid user)? (?P<user>\w+) from (?P<ip>\S+)`
Template=`${_DATA_}`
Attach=user
Attach=ip
The example config is executing a syslogrouter preprocessor followed by a regexattach preprocessor. The calling order is defined in the [Global] section.
#> ./test --help
Usage of ./preprocessortest:
-config-path string
Path to the plugin configuration
-data-path string
Optional path to data export file
-import-format string
Set the import file format manually
-verbose
Print each entry as its processed
An example execution of a preprocessor stack is:
#> ./preprocessortest -data-path /tmp/51780259054.json -config-path /tmp/recase.conf
INPUT: 100
OUTPUT: 100
PROCESSING TIME: 251.725404ms
PROCESSING RATE: 397.26 E/s
Adding the --verbose flag will cause the preprocessortest program to print every entry; if entries are not printable characters you may see garbage on the screen.
The preprocessortest program also enables debug mode for plugins by default, so any printf or println calls will output to standard out.
Available Preprocessors#
Preprocessor |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Attaches intrinsic values to entries per processor |
|
Decompress gzipped data in entries |
|
Parse and extract elements in JSON data |
|
Parse JSON array data and split the array into individual entries |
|
Parse JSON data and filter based on field values |
|
Parse JSON data and extract timestamps from specific field values |
|
Parse Syslog (RFC5424/RFC3164) data and route to specific tags based on field values |
|
Parse CSV data and route to specific tags based on column values |
|
Route entries to specific tags based on regular expression matches |
|
Route entries to specific tags based on source IP or value |
|
Route entries to specific tags based on the tag, or a combination of tag and either IP address or network |
|
Perform complex timestamp processing using regular expressions |
|
Perform data extractions and repacking using regular expressions |
|
Drop or pass data based on a regex |
|
Perform regex-based find and replace operations on entries |
|
Forward entries using TCP or UDP connections |
|
Forward entries using a Gravwell ingest connection |
|
Simple dropping preprocessor, it stops all entries from moving through the preprocessor chain |
|
Cisco ISE multi-message reconstruction preprocessor |
|
Preprocessor to adapt Corelight JSON logs to Zeek TSV data |
|
Preprocessor that loads interpretted code to perform custom preprocessing actions |