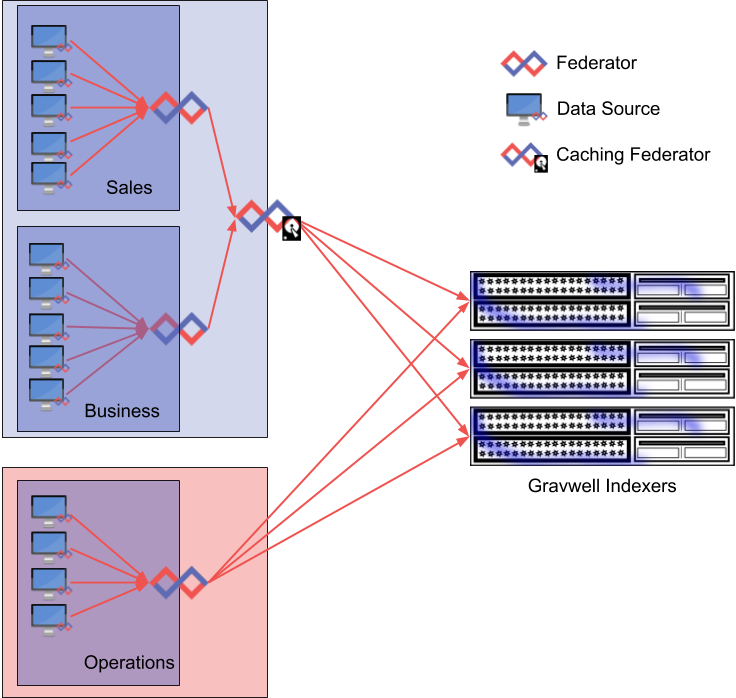
The Gravwell Federator#
The Federator is an entry relay: ingesters connect to the Federator and send it entries, then the Federator passes those entries to an indexer. The Federator can act as a trust boundary, securely relaying entries across network segments without exposing ingest secrets or allowing untrusted nodes to send data for disallowed tags. The Federator upstream connections are configured like any other ingester, allowing multiplexing, local caching, encryption, etc.
IngestListener Examples#
[IngestListener "enclaveA"]
Ingest-Secret = CustomSecrets
TLS-Bind = 0.0.0.0:4024
TLS-Certfile = /opt/gravwell/etc/cert.pem
TLS-Keyfile = /opt/gravwell/etc/key.pem
Tags=windows
Tags=syslog-*
[IngestListener "enclaveB"]
Ingest-Secret = OtherIngestSecrets
Cleartext-Bind = 0.0.0.0:4023
Tags=apache
Tags=bash
Use Cases#
Ingesting data across geographically diverse regions when there may not be robust connectivity
Providing an authentication barrier between network segments
Reducing the number of connections to an indexer
Controlling the tags a data source group can provide
Providing a connection buffer between a large number of ingesters and indexers
Installation#
If you’re using the Gravwell Debian repository, installation is just a single apt command:
apt-get install gravwell-federator
Otherwise, download the installer from the Downloads page. Using a terminal on the Gravwell server, issue the following command as a superuser (e.g. via the sudo command) to install the Federator:
root@gravserver ~ # bash gravwell_federator_installer.sh
The Federator will almost certainly require configuration for your specific setup; please refer to the following section for more information. The configuration file can be found at /opt/gravwell/etc/federator.conf. The Federator will also read configuration snippets from its configuration overlay directory (/opt/gravwell/etc/federator.conf.d).
Example Configuration#
The following example configuration connects to two upstream indexers in a protected network segment and provides ingest services on two untrusted network segments. Each untrusted ingest point has a unique Ingest-Secret, with one serving TLS with a specific certificate and key pair. The configuration file also enables a local cache, making the Federator act as a fault-tolerant buffer between the Gravwell indexers and the untrusted network segments.
[Global]
Ingest-Secret = SuperSecretUpstreamIndexerSecret
Connection-Timeout = 0
Insecure-Skip-TLS-Verify = false
Encrypted-Backend-target=172.20.232.105:4024
Encrypted-Backend-target=172.20.232.106:4024
Ingest-Cache-Path=/opt/gravwell/cache/federator.cache
Max-Ingest-Cache=1024 #1GB
Log-Level=INFO
[IngestListener "BusinessOps"]
Ingest-Secret = CustomBusinessSecret
Cleartext-Bind = 10.0.0.121:4023
Tags=windows
Tags=syslog
[IngestListener "DMZ"]
Ingest-Secret = OtherRandomSecret
TLS-Bind = 192.168.220.105:4024
TLS-Certfile = /opt/gravwell/etc/cert.pem
TLS-Keyfile = /opt/gravwell/etc/key.pem
Tags=apache
Tags=nginx
Max-Past-Timestamp-Delta=48h
Max-Future-Timestamp-Delta=24h
Ingesters in the DMZ can connect to the Federator at 192.168.220.105:4024 using TLS encryption. These ingesters are only allowed to send entries tagged with the apache and nginx tags. Ingesters in the business network segment can connect via cleartext to 10.0.0.121:4023 and send entries tagged windows and syslog. Any mis-tagged entries will be rejected by the Federator; acceptable entries are passed to the two indexers specified in the Global section.
Any entries received on the DMZ listener with timestamps more than 48 hours in the past or 24 hours in the future will have the timestamp replaced with the current time; setting these options can be helpful when ingesters you do not control may be sending data with poorly-extracted timestamps (it is surprisingly common to receive entries timestamped 1970-01-01).
IngestListener Configuration#
An IngestListener can be configured to listen on any combination of cleartext connections, TLS connections, or Unix named pipe connections. Each listener must contain at least one listener and may only define a single instance of any listener type; this means a single IngestListener cannot listen on multiple cleartext connections. To enable multiple listeners of the same type, define multiple IngestListener blocks.
Each IngestListener supports the following configuration options:
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Ingest-Secret |
string |
Ingest authentication token |
Tags |
string (list) |
Tags allowed to be ingested, wildcards are supported |
Preprocessor |
string (list) |
Name of a preprocessor to apply to ingested data, many Preprocessor parameters can be applied |
Pipe-Bind |
string |
Path to a Unix named pipe listener |
Cleartext-Bind |
string |
IP:Port which defines a port and optional IP address for cleartext connections |
TLS-Bind |
string |
IP:Port which defines a port and optional IP address for TLS connections |
Cert-File |
string |
Path to an X509 public certificate file for use in TLS listeners |
Key-File |
string |
Path to an X509 private key file for use in TLS listeners |
Low-Memory-Mode |
bool |
Optional mode to enable lower memory usage in transport buffers (default false) |
Disable-Ingester-Tracking |
bool |
Optional mode to disable downstream ingester tracking (default false) |
Max-Past-Timestamp-Delta |
string (duration) |
Optional; if set to a valid duration (e.g. “24h”), any entries received by this listener with a timestamp more than this duration into the past will have the timestamp replaced with the current time. |
Max-Future-Timestamp-Delta |
string (duration) |
Optional; if set to a valid duration (e.g. “24h”), any entries received by this listener with a timestamp more than this duration into the future will have the timestamp replaced with the current time. |
The Low-Memory-Mode and Disable-Ingester-Tracking options are useful when supporting many transient ingesters or when you expect many hundreds or thousands of ingesters to connect. The Gravwell ingest system is designed to be low latency and high throughput, which incurs some additional memory overhead as we allocate larger read buffers. The larger read buffers may make it difficult to support many ingesters, so these options allow you to reduce ingest overhead at the expense of potentially slower ingest rates and the loss of ingester config tracking.
Troubleshooting#
Common configuration errors for the Federator include:
Incorrect Ingest-Secret in the Global configuration
Incorrect Backend-Target specification(s)
Invalid or already-taken Bind specifications
Enforcing certification validation when upstream indexers or Federators do not have certificates signed by a trusted certificate authority (see the
Insecure-Skip-TLS-Verifyoption)Mismatched Ingest-Secret for downstream ingesters