Kafka Federator#
Gravwell also provides a Kafka Federator, that behaves exactly like the Federator, except that it uses Kafka as an upstream transport. Ingesters can connect to it just as with Federator, and ingested entries will be put into Kafka Topics as messages.
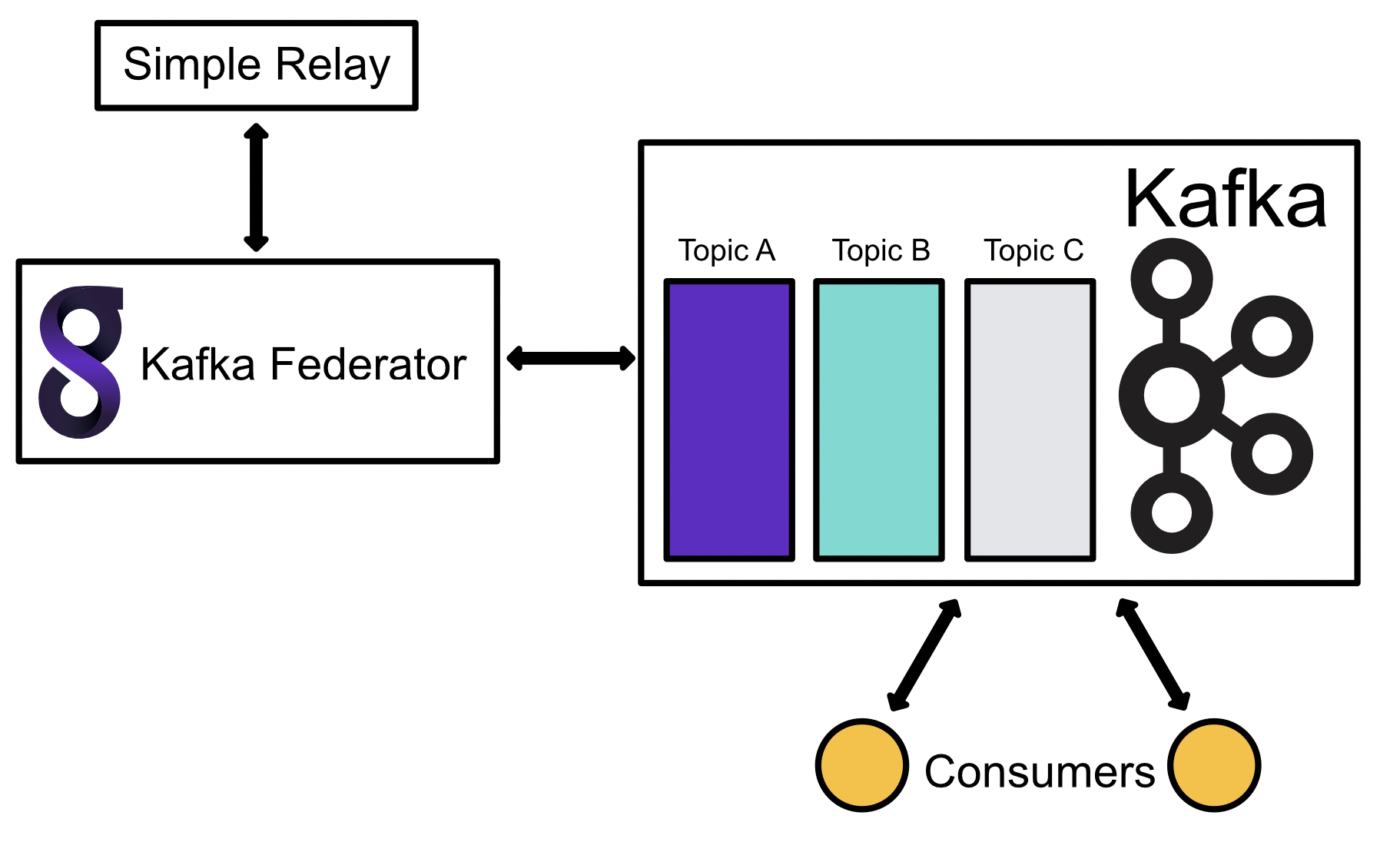
The Kafka Federator can be paired with the Kafka Consumer to read messages from a topic and ingest them into a Gravwell indexer.
Installation#
To install the Debian package, make sure the Gravwell Debian repository is configured as described in the quickstart. Then run the following command as root:
apt update && apt install gravwell-kafka-federator
To install the Redhat package, make sure the Gravwell Redhat repository is configured as described in the quickstart. Then run the following command as root:
yum install gravwell-kafka-federator
To install via the standalone shell installer, download the installer from the downloads page, then run the following command as root, replacing X.X.X with the appropriate version:
bash gravwell_kafka_federator_installer_X.X.X.sh
You may be prompted for additional configuration during the installation.
The Docker image is available on Dockerhub.
Configuration#
The configuration file is at /opt/gravwell/etc/kafka_federator.conf. The Federator will also read configuration snippets from its configuration overlay directory (/opt/gravwell/etc/kafka_federator.conf.d).
Kafka Federator defines listeners and Kafka headers. A listener is similar to a Federator listener, in which ingesters may connect and send entries. Listeners also define what topic to publish messages on. A header sets arbitrary key value pairs in the generated Kafka header.
Additionally, the global section defines a group leader to connect to and a partition. Because the Kafka Federator is designed to send data to a Kafka broker rather than a Gravwell indexer, the [Global] section of the configuration file is different than typical Gravwell ingesters. The following configuration parameters are available in the [Global] section:
Configuration Parameter |
Description |
Required |
|---|---|---|
Leader |
Host:Port that specifies a Kafka broker leader to connect to |
X |
Partition |
Partition ID |
Defaults to 0 |
Enable-Gravwell-Tag |
Enables the internal Gravwell tag logging through Kafka |
|
Gravwell-Tag-Topic |
Specifies the topic to send Gravwell tag entries |
Required when Enable-Gravwell-Tag=true |
Timeout |
Timeout when connecting to Kafka and sending values |
Defaults to 1 second |
Log-File |
Specify log file for status and error logs |
|
Log-Level |
Logging level |
|
Entry-Buffer-Len |
Set the internal memory buffer for relaying entries |
|
Cache-Depth |
Specify how many entries can be kept in flight before a forced flush |
|
Cache-Mode |
Set the caching strategy |
|
Ingest-Cache-Path |
Specify the cache storage location |
|
Max-Ingest-Cache |
Specify the maximum disk available for a local cache |
|
Use-TLS |
Enable TLS when connecting to Kafka |
|
Insecure-Skip-TLS-Verify |
Allow invalid certificates when connecting via TLS (INSECURE) |
|
Auth-Type |
Enable SASL authentication and specify the mechanism |
|
Username |
Specify username for Kafka SASL authentication |
|
Password |
Specify password for Kafka SASL authentication |
Authentication#
The Kafka Federator supports the following SASL authentication mechanisms: PLAIN, SCRAMSHA256, and SCRAMSHA512. To enable authentication set the Auth-Type configuration parameter to the desired authentication type and provide a Username and Password. The following is a valid configuration snippet from the [Global] section of a Kafka Federator that is configured to use plaintext authentication:
[Global]
Auth-Type=plain
Username=TheDude
Password="a super secret password"
Valid Auth-Type options are plain, scramsha256, and scramsha512.
Headers#
The Kafka Federator supports the ability to set headers in Kafka Messages. Headers can either be derived from entries using special variables or static values. This can be useful when the Federator may be feeding non-Gravwell endpoints like Splunk.
Headers are enabled by creating a KafkaHeaders configuration and then enabling it in an ingest listener using the Kafka-Header-Set configuration parameter. For example we might want to set a static header value to assist with downstream routing as well as the source and tag. The configuration for the KafkaHeaders would look like so:
[KafkaHeaders "routingheaders"]
source=$SRC
gravwelltag=$TAG
routeid="business network"
When enabled on a listener this configuration will attach three header values to each message in Kafka. The source and gravwelltag headers will extract their values from the Gravwell entries, creating text representations of the source and tag, the routeid value is a static string “business network” which might be useful for a consumer looking to attach metadata to entries. The entry timestamp attached to Gravwell entries is always copied to the Kafka value.
Kafka headers can be populated with special variables, as shown in the example above.
Variable |
Description |
|---|---|
$TAG |
The entry tag |
$SRC |
The entry source |
Example#
This example generates a single listener that allows tags “windows” and “syslog”. Messages are published to the “testing” Kafka topic. A header is also defined that sets several key/value pairs. Note that the special $TAG, $SRC values are available for use in setting values in a Kafka header.
[Global]
Leader=10.10.0.1:9092
Partition=0
Log-Level=INFO
Log-File=/opt/gravwell/log/kafka_federator.log
[IngestListener "enclaveA"]
Ingest-Secret = CustomSecrets
Cleartext-Bind = 0.0.0.0:4423
Tags=windows
Tags=syslog
Topic=testing
Kafka-Header-Set=headers
[KafkaHeaders "headers"]
TAG=$TAG
SRC=$SRC
source=$SRC
foo=bar